Privileges
Design Pattern
Alternate titles: Powers.
Problem summary
Give users a way to reach their goal more quickly than they could before
Example
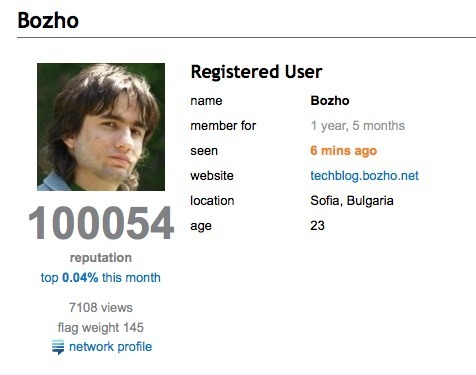
▲ This user on stackoverflow.com has a flag weight of 145 - actions of this user will weigh much more than the actions of a newly signed up user.
Usage
- Use to distinguish between rookie, normal, and power users.
- Use to promote users that contribute quality content.
- Use when your users are naturally divided into specific roles, where some powers are a natural given fact.
This card is part of the Persuasive Patterns printed card deck
The Persuasive Patterns Card Deck is a collection of 60 design patterns driven by psychology, presented in a manner easily referenced and used as a brainstorming tool.
Get your deck!Solution
Provide a way for users to earn a set of powers that will allow them to reach their goal more quickly than they could have before. This pattern is often used in combination with Unlocking features
In web design, there are two common roles that are most often rewarded with special powers: The contributor and curator role.
Reward the contributor and curator roles
A contributor is a person who posts stories, uploads images, makes comments, and in general adds content to a website. Contributions are essential for a website to have interesting content, however without filtering for quality content too many poor contributions can flood a website with otherwise good content. This is where the curator comes in.
Curators are the users who make an effort in defining what is quality content and what is not. They vote quality content up, flag content with profanity, and vote poor quality down.
The relationship between the contributors and curators are often intertwined in that users with a proven track record of quality content are immediately promoted more than a rookie user or a user with a poor track record.
Grant roles
Awarding users with specific powers in a community can help provide users with a specific role (moderator, curator, etc.) and thus help give a sense of purpose, place and a sense of belonging in a community.
Instil a sense of self-determination
According to self-determination theory, people are able to become self-determined when their needs for competence, connection, and autonomy are fulfilled. Granting privileges to individuals can provide a path that will allow them to go their own ways, have a place and connection in a community, and grow their competence to interact with as they administer their powers3.
Common powers given to users
There are several ways to empower users. Here is a list of common powers attained:
- Vote comments up or down
- Power vote – a user’s vote counts double, triple, or quadruple the vote of regular users
- Delete resources – content, comments, posts, images, users
- Create content – power to post specific types of content: polls, quizzes, or other specialized content
- Contributions immediately promoted as quality – no need to wait for other users to vote it up
Rationale
Becoming more powerful is something that everyone desires in real life. Being giving special powers, no matter in what form, all have in common that they give you a way to reach your goal more quickly than you could before1.
Provide temporary or permanent benefits or extra abilities to let users reach their goal faster.
Providing users with powers to reach existing goals faster or embrace new ones, is a common technique used in persuasive design and gamification to boost autonomy, mastery, and belonging: the tenets of self-determination theory in social psychology.
1 Jesse Schell, “The Art of Game Design – A Book of Lenses”, Carnegie Mellon University
3 Ryan, R. M.; Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist. 55 (1): 68–78.
4 Privileges at Learning Loop
5 Self-Determination Theory by Anders Toxboe at Learning Loop
More examples of the Privileges pattern See all 2 example screenshots

User Interface Design Patterns
- Forms
- Explaining the process
- Community driven
- Tabs
- Jumping in hierarchy
- Menus
- Content
- Gestures
- Tables
- Formatting data
- Images
- Search
- Reputation
- Social interactions
- Shopping
- Increasing frequency
- Guidance
- Registration
Persuasive Design Patterns
- Loss Aversion
- Other cognitive biases
- Scarcity
- Gameplay design
- Fundamentals of rewards
- Gameplay rewards
