Investment Loops
Design Pattern
Alternate titles: Hook Model, Habit Loop.
This card is part of the Persuasive Patterns printed card deck
The Persuasive Patterns Card Deck is a collection of 60 design patterns driven by psychology, presented in a manner easily referenced and used as a brainstorming tool.
Get your deck!Solution
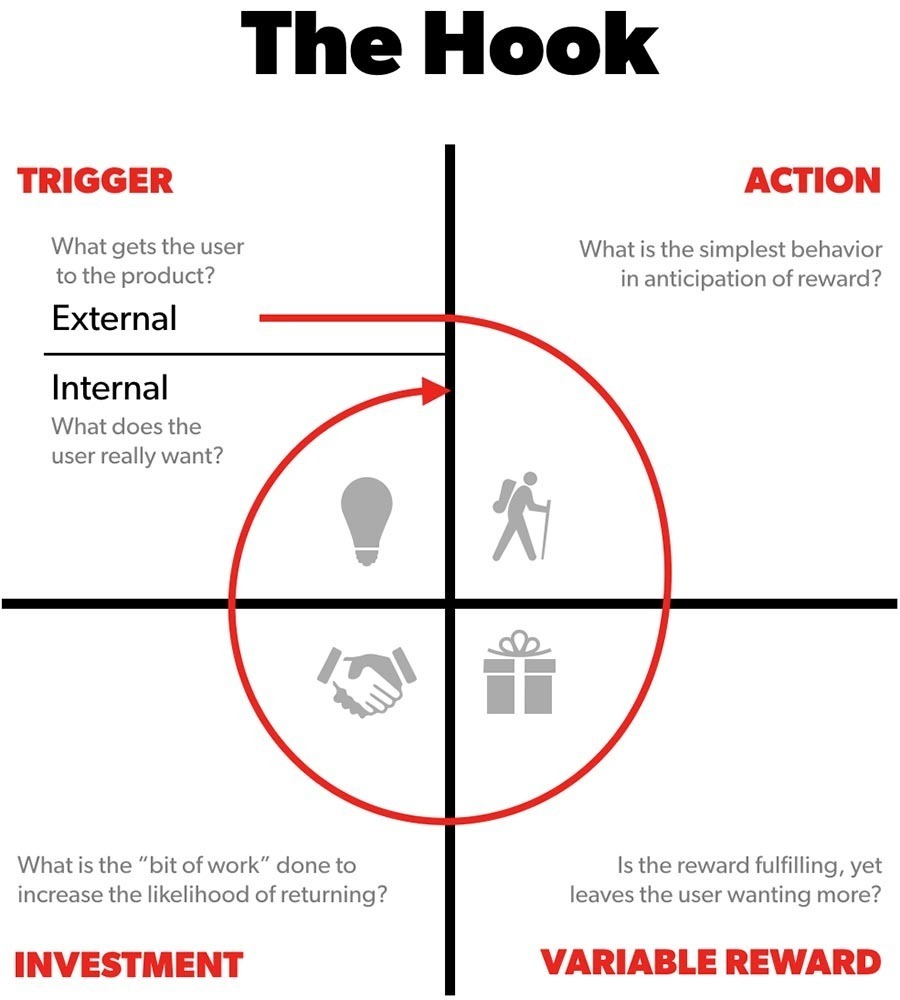
Find ways for users to invest time, money, information, or effort into a product to set themselves up for future rewards. By sending a message to a friend, users set themselves up for receiving a reply – a future reward and trigger to get back into your product and conduct new behavior. In this way a habit loop is formed. With the anticipation of a future reward to come, the likelihood of users coming back is greater.
- Get people to invest. Let the user do work (investment) in the anticipation of future rewards (not immediate) that make the likelihood of users coming back for another pass in the loop more likely. Investments like this can help set up the trigger that is going to help bring users back int the loop. Consider what the simplest behavior is the the user can do in anticipation of a reward.
- Investments store value. For each pass in the loop, more value is stored in the product (user’s investments), effectively improving the product with use.
- Map out triggers. Consider what external triggers need to be in place to get the user to the product, but equally important how can you setup triggers within your product (internal triggers) that gets your users coming back.
Rationale
Setting up cycles of recurring triggers, actions, and investments will possibly set users up for coming back for more.
In his bestselling book, Nir Eyal proposed a model for implementing addictive habit loops into tech products where users set invest their time and effort into a product and if designed the right way, set themselves up for recurring rewards that trigger them to return for more. His model is inspired by BJ Fogg’s Behavior Model.
1 Fogg, BJ (2009). A behavior model for persuasive design, Persuasive ’09: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Persuasive Technology. Pages 1–7
2 Eyal & Hoover (2014). Hooked: How to build habit-forming products. Penguin Canada.
3 Making the Hook Model actionable by Anders Toxboe
User Interface Design Patterns
- Forms
- Explaining the process
- Community driven
- Tabs
- Jumping in hierarchy
- Menus
- Content
- Gestures
- Tables
- Formatting data
- Images
- Search
- Reputation
- Social interactions
- Shopping
- Increasing frequency
- Guidance
- Registration
Persuasive Design Patterns
- Loss Aversion
- Other cognitive biases
- Scarcity
- Gameplay design
- Fundamentals of rewards
- Gameplay rewards