Password Strength Meter
Design Pattern
Problem summary
You want to make sure your users' passwords are sufficiently strong in order to prevent malicious attacks.
Example
Usage
- Use when you want your users to choose passwords for their user accounts that are hard to break or guess by either human or computerized help.
- Use when you want to increase the complexity of your users’ passwords and raise the barrier for attackers tampering with your system.
- Use when you want to be sure that your users know what a good password is and that their chosen password follows such guidelines.
Solution
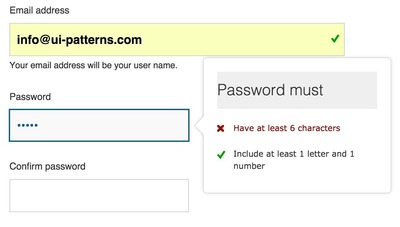
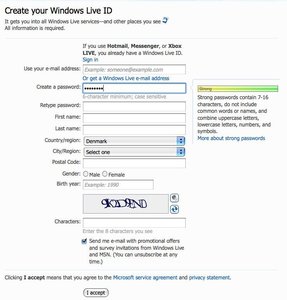
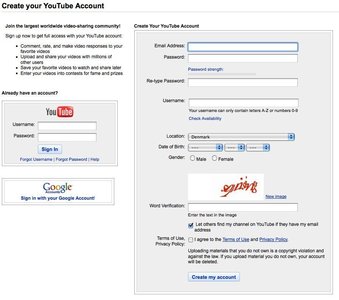
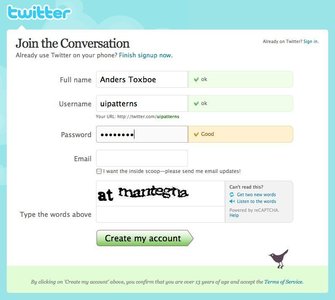
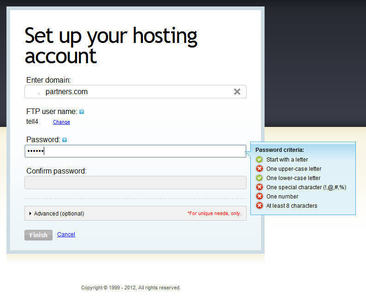
A password’s strength is measured according to predefined rules and is displayed using a horizontal scale next to the input field. If the password is weak then only a small portion of the horizontal bar is highlighted. The greater the strength of the password the more the horizontal bar is highlighted.
The password strength is also appropriately indicated by coloring the bar in a color associative with good or bad: Green indicating a strong password and red indicating a weak password.
How strong a password?
The definition of a strong password can be intensely argued. A forced complex password at first glance only spells increased security, but forcing too complex and rigid rules on password can have the opposite effect. As passwords are forced to be complex, they also become increasingly harder to remember by the user. This occasionally leads to a self-destruction of the increased security, as some users simply write it down on a small sticky note and paste it up on their screen in order to remember their new complex password. This is especially a problem in places with the policy of forced password renewal every 3 months.
What is a strong password?
With the above mentioned in mind, I should stress that a sufficiently strong password does not necessarily need to fulfill all of the rules below, but merely a few will do. Consider the following rules, for each rules followed add a point to the passwords strength level (so that 0 points is the weakest, and 5 is the strongest). UI-patterns.com defines a strong password when it…:
- Has more than 8 characters
- Contains both lowercase and uppercase letters
- Contains at least one numerical character
- Contains special characters
- Has more than 12 characters
This would result in 6 levels of password strength depending on how many of the above mentioned criteria are being met.
Dictionary attacks
While the above mentioned password check can easily be done using only client-side javascript, it does not prevent against dictionary attacks. To ease the memorization of passwords, people tend to use real words as passwords and merely substitute characters with numbers or special characters. An example of such a password could be “P@ssw0rd”, which really isn’t a strong password. Modern password breaking software is fairly good at guessing such number/letter substitutions. To check against such strength, you would need to do ajax calls that would check with your own dictionary if the password was strong or not.
Choosing an appropriate level of password strength
You need to determine the password strength and complexity according to what you want to protect. You need to draw the line somewhere. For 99% of the content out there it can easily be argued that merely the first 2 or 3 rules mentioned above will be sufficient.
General guidelines on choosing a password
- Use a password of a seemingly random selection of letters and numbers
- Use a password that you can type without you having to look at the keyboard (decreases possibility of people stealing your password)
- Change your password regularly
- Do not use your network ID in any form (capitalized, reversed, doubled, etc.)
- Do not use your first, middle or last name or anyone else’s in any form.
- Do not use your initials or any nicknames you or somebody else might have.
- Do not use a word contained in any dictionary (English or foreign), spelling list, abbreviation list, etc.
- Do not use information that people can easily obtain about you (license plate, pet name, date of birth, telephone numbers)
- Do not use password of all alphabetical characters or only numeric characters – mix them up.
- Do not use keyboard sequences (for instance qwerty or asdf)
Rationale
By showing a password strength meter beside the password field, the user is forced to consider using a password with an appropriate strength. By putting a minimum level of password strength you can even use the password strength meter to force a heightened security to your website.
Using a password strength indicator on the website, adds another level of security is added to the site. This not only makes the current users of the site feel more secure, but potential clients might use this as a requisite when deciding to conduct business with a company.
More examples of the Password Strength Meter pattern See all 6 example screenshots
User Interface Design Patterns
- Forms
- Explaining the process
- Community driven
- Tabs
- Jumping in hierarchy
- Menus
- Content
- Gestures
- Tables
- Formatting data
- Images
- Search
- Reputation
- Social interactions
- Shopping
- Increasing frequency
- Guidance
- Registration
Persuasive Design Patterns
- Loss Aversion
- Other cognitive biases
- Scarcity
- Gameplay design
- Fundamentals of rewards
- Gameplay rewards

4 comments
Jasper Kennis on Mar 20, 2008
There is a downside to this method: some of them make make me use rediculously long passwords, for they do indeed check the number of different characters used. Even though it deserves a positive vote: it’s extra feedback, always a good thing, and it might prevent the use of bob as a passy too.
casino online on Nov 25, 2010
For illustration purposes I have created a sample enquiry form which the website user can submit their enquiry and the form will send an email to the site administrator.
Ken on Jan 08, 2011
Rating:
0-9: Pathetically weak – Can get hacked very quickly
10-19: Extremely weak – Easy to hack
20-29: Very weak – A bit prone to hacking
30-39: Weak – Good enough if you are in a hurry
40-49: So-so – Fairly safe
50-60: Average – Quite safe
61-70: Fair – Extremely safe
71-80: Strong – Unbelievably safe
81-90: Very strong – Almost the safest
91-100: Unbelievably strong -Couldn’t be safer
Jan on Mar 09, 2011
I think there is a downside to the password strenght meter from a user experience perspective and sometimes also a business perspective.
What we’ve seen in research is that some users gets obsessed with achieving the “strong” value for the password which means they are not very likely to remember their password when logging in the next time.
This causes them to use the retrieve password functionality and if no such functionality is in place they will have to contact customer service. In worst case they might give up logging in which might lead to us losing this user as a customer.
My conclusion is that before implementing this type of functionality you need to analyze the pros and cons. Do you really store the type of sensitive user data on your website that needs this security?
Comments have been closed